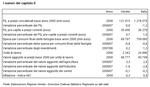
The year 2009 recorded a decrease of 0.8 % in global wealth, 2.4% in US GDP, and 4.1% in the GDP of the euro area.
Italy ended 2009 with a -5.1% decline in GDP; like Germany, Italy experienced a steep decline in productivity, caused by the contraction in international trade, due to the size of its manufacturing industry.
The trough was certainly reached in the first semester of 2009 and can be seen in the decline in all economic indicators; however, since March, the Italian economy has been on course toward improvement. The decline in the first quarter was certainly the result of the fall in investment and of household consumption.
Official regional data ends in 2008 at the beginning of the international recession, when the Gross Domestic Product of Veneto had fallen by 0.8%. In national terms, the economy of Veneto held up better than both the Italian average and the regions considered its economic rivals, Lombardia and Piemonte. Once again in 2008, Veneto was found to be the third largest regional contributor to Italy's GDP: the region contributed 9.4% of the national total, behind Lazio and Lombardia. This result is thanks to growth in agriculture and the strength of the service sector, despite the negative contribution of industry.
Household spending declined rather modestly, while GDP per inhabitant, equal to 30,456 euro compared to the 26,278 euro on a national level, grew.
For 2009 the Prometeia research institute estimates that the downturn in GDP in Veneto is in line with the national trend, and forecasts growth by the end of 2010.
The result for 2009 is attributed principally to the crisis in manufacturing, whose value added is expected to decrease by about 13 percentage points, and to the decline in the construction sector.
In Veneto in 2009 inflation was on average lower than the national rate.
(Chapter 6 in figures)