5. The figures tell the story
|
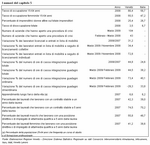
In the last few months of 2008, Italy's employment rate stopped rising; in Veneto, however, the employment rate in 2008 grew by almost 2% on the 2007 rate.
As a result, the Italian employment rate for 2008 did not change compared to 2007 as it was still 58.7%. Conversely, in 2008 Veneto had an employment rate of 66.4%, up 0.6% compared to 2007 and higher than in EU27 (65.9%). While employment stalled, the state of emergency became clear as unemployment spread in Italy. The number of people looking for work in Veneto is also rising: +8.2% on 2007 (Italian figure: +12.3%). Unemployment rates are also increasing; Veneto, however, still maintains its low level (3.5% against 3.3% in 2007) and is a long way off the national average (6.7%, up 0.6% on 2007). Redundancies are also on the up, especially in Veneto's small-sized enterprises in the most recent period: between November 2008 and March 2009, in Veneto the number of people newly registered on mobility lists rose by 62%. Major recourse to Wage Guarantee Funds is also being made. In March 2009 in Italy, almost 59 million hours were authorised by the Wage Guarantee Fund (i.e. an average of more than 427,000 workers covered by a Wage Guarantee Fund every day), 38.2% more than the previous month and almost four times above the figure for the same time last year. In Veneto just under 3.5 million hours were granted (the Wage Guarantee Fund equivalent of 24,500 workers), 44.5% more than in February and almost double the figure for March 2008. (Chapter 5 in figures) |
|
Data processed by the Statistics Office of Regione Veneto are collective property; reproduction of this material is authorised for non-commercial purposes only, provided the source "Regione Veneto - Regional Statistics System Management" is acknowledged.
English translation by the University of Padova Language Centre.